DNS Recursive Query in Action | DNS | Domain Name System | Udemy Course | CSEPracticals
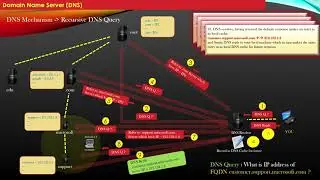
A recursive query in the context of networking refers to a type of DNS (Domain Name System) query where the DNS resolver, typically a client or a DNS server, requests information from another DNS server to resolve a domain name. This process continues until the resolver receives a fully resolved IP address or an error.
Here's a step-by-step explanation of how a recursive DNS query works:
Client Initiates Query: When a user enters a domain name (e.g., www.example.com) in a web browser, the local DNS resolver (often provided by the Internet Service Provider or configured by the user) initiates a recursive query.
Contacting Root DNS Server: The resolver first contacts a root DNS server. The root DNS server responds with a referral to the appropriate top-level domain (TLD) DNS server for the requested domain (e.g., ".com" for www.example.com).
Contacting TLD DNS Server: The resolver then contacts the TLD DNS server, which responds with a referral to the authoritative DNS server for the second-level domain (e.g., "example.com").
Contacting Authoritative DNS Server: The resolver contacts the authoritative DNS server for the specific domain (e.g., "example.com") and requests the IP address associated with the domain name.
Resolution and Response: The authoritative DNS server responds with the IP address, and the resolver caches this information for future use.
Response to Client: The final IP address is sent back to the client, allowing the client's device to connect to the desired web server.
In a recursive query, the DNS resolver is responsible for making multiple requests to different DNS servers until it obtains the final resolution. This process allows for efficient resolution of domain names, and the DNS resolver often caches the results to speed up future queries for the same domain.
It's worth noting that not all DNS queries are recursive. Some DNS queries are non-recursive, where the DNS server is expected to provide the best answer it can without referring the requester to other servers. Recursive queries are more common in everyday internet usage.
Visit : www.csepracticals.com
Watch video DNS Recursive Query in Action | DNS | Domain Name System | Udemy Course | CSEPracticals online, duration hours minute second in high quality that is uploaded to the channel CSE Practicals 08 January 2024. Share the link to the video on social media so that your subscribers and friends will also watch this video. This video clip has been viewed 78 times and liked it 1 visitors.