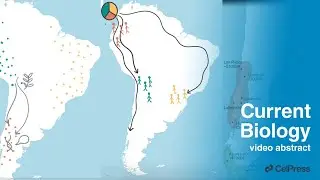
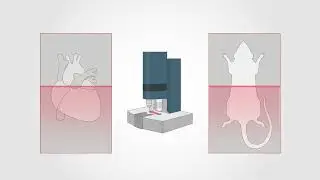
The buzz on bees: Danger triggers a dopamine dip! / Curr. Biol., Apr. 13, 2023 (Vol. 33, Issue 10)
New research shows that both positive and negative experiences can impact honeybee brain dopamine levels. Elevated dopamine levels are seen in bees when first discovering rewarding food or when performing waggle dances to recruit nestmates to food. However, the receipt of an inhibitory signal (the stop signal), triggered by negative events at the food source, can decrease dopamine levels and reduce waggle dancing. Increasing dopamine levels can reduce aversive effects of an attack. These findings demonstrate the complex integration of colony information and neural mechanisms in honeybees.
Check out the paper at http://www.cell.com/current-biology/f....
S. Dong, G. Gu, T. Lin, Z. Wang, J. Li, K. Tan, and J.C. Nieh (2023). An inhibitory signal associated with danger reduces honeybee dopamine levels. Curr. Biol. 33.
And read more great research at http://www.cell.com/current-biology/home.
Watch video The buzz on bees: Danger triggers a dopamine dip! / Curr. Biol., Apr. 13, 2023 (Vol. 33, Issue 10) online, duration hours minute second in high quality that is uploaded to the channel Cell Press 13 April 2023. Share the link to the video on social media so that your subscribers and friends will also watch this video. This video clip has been viewed 949 times and liked it 12 visitors.