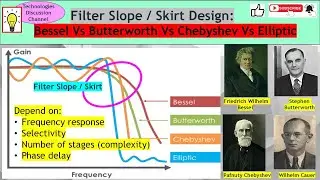
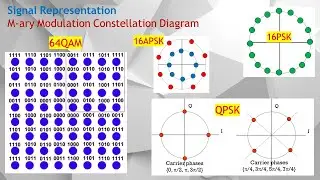
Digital Modulation Part 6. How Quadrature Amplitude Modulation, QAM Achieves Better Throughput.
Digital Modulation playlist.
• Digital Modulation Part 1. How Data S...
16APSK (16-ary Amplitude Phase-Shift Keying) is a digital modulation scheme that combines both amplitude and phase modulation.
Two Concentric Rings consists of:
An inner ring with 4 or 8 phase-shifted symbols (constant amplitude).
An outer ring with 8 or 12 symbols (higher amplitude).
Common configurations: 4+12 APSK or 8+8 APSK.
Quadrature Amplitude Modulation (QAM) is a modulation technique that transmits digital data by simultaneously varying both the amplitude and phase of a carrier signal. This allows for higher data rates compared to using only amplitude or phase modulation, while also making more efficient use of bandwidth.
Quadrature amplitude modulation (QAM) is a family of digital modulation methods—and a related set of analog modulation techniques—widely used in modern telecommunications to transmit information. It conveys two analog message signals or two digital bit streams by modulating the amplitudes of two carrier waves. This modulation employs either amplitude-shift keying (ASK) for digital signals or amplitude modulation (AM) for analog signals.
The two carrier waves share the same frequency but are 90° out of phase (a condition called orthogonality or quadrature). The transmitted signal is formed by combining these two carriers. At the receiver, their orthogonality allows them to be coherently separated (demodulated).
A key feature of QAM is that the modulating signals have a low frequency/bandwidth compared to the carrier frequency, adhering to the narrowband assumption.
Смотрите видео Digital Modulation Part 6. How Quadrature Amplitude Modulation, QAM Achieves Better Throughput. онлайн, длительностью online в хорошем качестве, которое загружено на канал Technologies Discussion 02 Май 2025. Делитесь ссылкой на видео в социальных сетях, чтобы ваши подписчики и друзья так же посмотрели это видео. Данный видеоклип посмотрели 79 раз и оно понравилось 2 посетителям.