SQL : Constraints in Oracle or sql or sql server
Constraints In Oracle
Data validation before inserting the data into the table
1. Primary Key
-- It will not allow duplicate value
-- It will not allow null
-- Only one primary key in a table
e.g emp_id, prod_id, cust_id, user_id, account_no
composite Key:
cust_id+mobile_no ---gt Primary key(cust_id,mobile_no)
2. Not Null *mandatory field
-- It will not allow a null value
-- It will allow duplicate
e.g First_name
3. Unique Key
-- It will not allow duplicate
-- It will allow null
e.g mobile_no
4. Check
-- data validation
check (age gt=18)
5. Foreign Key
--- Relationship between two tables
-- It will accept duplicate value
-- It should be a primary key in another table
-- Any no of foreign key in a table
e.g foreign key (city_id) references city(city_id)
Violation:
Integrity constraint violated - parent key not found
6. Default
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Queries to practice:
create table customer
(
cust_id number(6) primary key,
cust_name varchar2(30) not null,
mobile_no number(10) unique check (length(mobile_no)=10),
age number(3) check (agegt=18),
city_id number(4) references city(city_id)
);
select * from city;
create table city
(
city_id number(4) primary key,
city_name varchar2(30)
);
insert into city values (10,'Chennai');
insert into city values (20,'Pune');
insert into city values (30,'Hyd');
insert into city values (40,'Delhi');
alter table city add primary key(city_id);
select * from city;
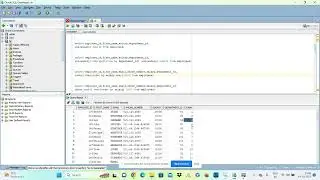
select * from customer;
insert into customer values (100000,'Arun',9090909090,28,20);
insert into customer values (100001,'Arun',8080808080,31,30);
insert into customer values (100002,'Vijay',5050505050,31,10);
insert into customer values (100003,'Ajith',2894738243,13,30);
insert into customer values (100004,'Ramesh',2894738789,31,60);
commit;
desc customer;
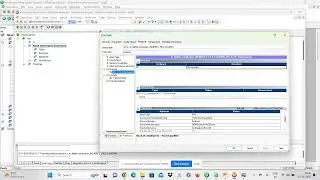
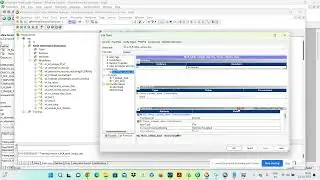
select * from all_constraints where owner='HR' and table_name='CUSTOMER';
select * from all_cons_columns where owner='HR' and table_name='CUSTOMER';
select
a.owner,a.constraint_name,a.constraint_type,b.table_name,b.column_name
from all_constraints a , all_cons_columns b where a.constraint_name=b.constraint_name
and a.owner='HR' and a.table_name='CUSTOMER';
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
On delete cascade
ALTER TABLE customer
drop CONSTRAINT SYS_C009091;
ALTER TABLE customer
ADD CONSTRAINT city_fk
FOREIGN KEY (city_id)
REFERENCES city(city_id)
ON DELETE CASCADE;
select * from all_constraints where owner='CORE' and table_name='CUSTOMER';
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
--Metadata tables will have all table & column level details
select * from all_tables where owner='HR';
select * from all_tab_columns where owner='HR' and column_name='SALARY';
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
create table country
(
cust_country_code varchar2(2) primary key,
country_name varchar2(30)
);
insert into country values('IN','India');
insert into country values('IN','USA');
drop table country;
create table customer
(
cust_id number(6),
cust_name varchar2(30) not null,
mobile_no number(10),
age number(3) check (agegt=18),
city_id number(4) references city(city_id),
primary key(cust_id,mobile_no)
);
insert into customer values (100000,'Arun',9090909090,28,20);
insert into customer values (100000,'Arun',9090909091,28,20);
insert into customer values (100000,'Arun',9090909090,28,20);
select * from customer;
Watch video SQL : Constraints in Oracle or sql or sql server online, duration hours minute second in high quality that is uploaded to the channel Technology with Kiran 08 January 2024. Share the link to the video on social media so that your subscribers and friends will also watch this video. This video clip has been viewed 42 times and liked it 0 visitors.