EMC Part 41. How to Reduce EMI with Signal Routing and Layer Partitioning for 1- or 2-Layer PCBs.
EMC playlist. Watch these video to understand more on EMC.
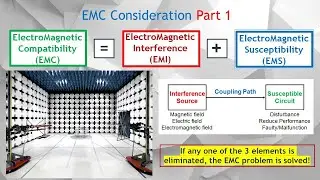
• EMC Part 1. Electromagnetic Compatibi...
How to Route the Signal Trace & Layer Partitioning (1 or 2 Layers) to Minimize EMI.
Single side (SS) or Double side (DS) PCB are preferred to multilayer PCB as they are cheaper, but SS / DS PCB demands more precautions in controlling EMI (and in particular radiated EMI) because loop sizes are larger in many circumstances. This is true for 1) power supply decoupling capacitor loop, 2) VCC to ground trace separation and 3) signal trace to ground trace loops.
Multilayer PCBs are the ultimate answer to PCB noise in general and especially to radiated EMI but are more costly, about 2 to 2.5 times that of DS PCB.
Crosstalk occurs when a wire or trace carrying a signal runs parallel to another conductor.
By mutual capacitance and inductance, the source conductor induces a small voltage into the victim conductor.
Crosstalk increases with the proximity of the source and the victim wires, increasing frequency (or decreasing rise time) and higher victim impedance.
Crosstalk may be reduced by:
Use of 2W rule.
Separate traces with minimum parallel run. Separate 2 parallel traces at least 2 mils (0.05 mm) of trace throughout the entire route.
Insert a guard trace (ground trace) between source and victim traces.
The basis of 2W rule is to provide adequate isolation between 2 traces so as to minimize coupling between the 2 traces. The 2W rule states that the minimum distance separation between the edge of 2 traces must be 2 times the width (W) of the trace. The drawback to provide for sufficient trace isolation is loss of PCB area.
For example, assume a clock line is 6 mils wide. No other trace can exist within a minimum of 2 x 6 mils = 12 mils edge-to-edge.
The advantages of having guard trace or shunt trace includes:
Reducing crosstalk between 2 traces by decreasing the mutual capacitive coupling.
Providing an additional “alternate low impedance return path” to the image plane return path.
The guideline is to avoid a 900 corner bend. When a trace makes a bend on the PCB, its capacitance/unit length increase, while its inductance/unit length decrease. This will result an effect similar to capacitive loading that occurs during signal transmission.
An edge that is less than 900 also reduces the amount of reflection for signal rounding the corner.
Watch video EMC Part 41. How to Reduce EMI with Signal Routing and Layer Partitioning for 1- or 2-Layer PCBs. online, duration 16 minute 40 second in high quality that is uploaded to the channel Technologies Discussion 21 May 2023. Share the link to the video on social media so that your subscribers and friends will also watch this video. This video clip has been viewed 710 times and liked it 8 visitors.